Pieter Delobelle
I'm dr. ing. Pieter Delobelle, AI researcher on LLM pretraining, tokenization & AI safety at KU Leuven and Pleias. Previously, I worked at Aleph Alpha on LLM inference, LLM steering at Apple and created Dutch language models. My research has been covered in Wired, De Tijd, VTM Nieuws, MIT Technology Review, De Morgen, and more. I also frequently give talks on AI and language models.News
April 23, 2026 I will give a half-day lecture on safety and fairness in LLMs. February 11, 2026 I will give a talk on building LLM inference from scratch at AI Tinkerers Ghent. January 26, 2026 I joined Pleias to work on synthetic data and small language models 🥖🇫🇷. January 24, 2026 I was interviewed live on VTM Nieuws about LLM hallucinations. December 12, 2025 I gave a talk at UGent on steering LLMs. December 11, 2025 I gave a talk on Dutch LLMs at the Wintercircus in Ghent. November 19, 2025 Our paper on neurosymbolic bias mitigation got accepted at AAAI 2026 🎉. October 15, 2025 I talked about our work on safety and fairness in LLMs at Flanders AI Research Day. September 24, 2025 I gave a talk on our Dutch LLMs at VUB's Ada Lovelace Lectures. September 10, 2025 I released a library for distributed LLM inference: llmq. View older newsHighlighted projects
NanoGPT-inference
LLM inference from scratch
LLM inference, the engineering behind serving LLMs efficiently and economically, is becoming increasingly important. In this post, I'll show you how to speed up LLM inference with various techniques. I also release the code of each inference engine as a simple extension to Karpathy's NanoGPT.
Introducing llmq
A Scheduler for Batched LLM Inference
llmq is a Python library that efficiently performs batched inference with millions of jobs using self-hosted open-source models. Built on RabbitMQ for reliable queueing, llmq handles the complex logic of batching, checkpointing, and restart mechanisms that are typically needed for large-scale synthetic data generation. With vLLM as the inference engine, it optimizes for total throughput rather than per-request latency, making it ideal for research, data generation, and scientific evaluations where you need to process massive datasets efficiently.
Metrics for What, Metrics for Whom?
Assessing Actionability of Bias Evaluation Metrics in NLP
In our EMNLP paper, we investigate the critical but often overlooked concept of "actionability" in NLP bias measures - essentially, how useful these metrics are for taking concrete steps to address bias. Through analyzing 146 papers on bias measurement in NLP, we discovered that crucial elements like intended use cases and reliability assessments are frequently missing or unclear, creating a significant gap between measuring bias and actually addressing it. Based on these findings, we propose new guidelines for developing and documenting bias metrics that can more effectively drive real-world improvements in NLP systems.
Trans-Tokenization
Language Adaptation of LLMs for Low-Resource NLP
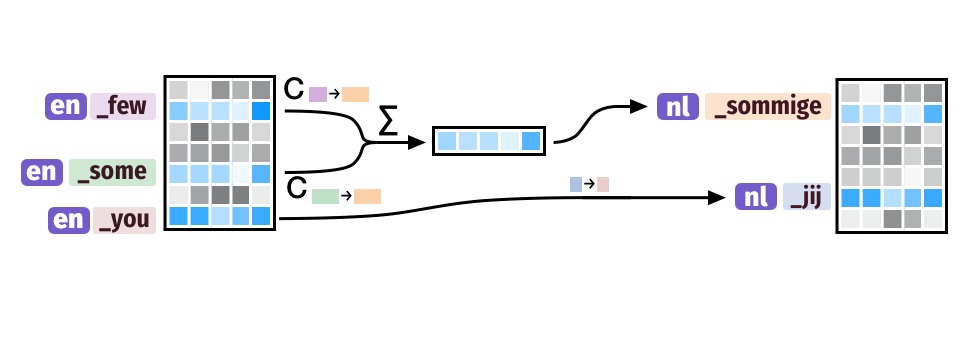
we present a novel cross-lingual vocabulary transfer strategy, trans-tokenization, designed to adapt a high-resource monolingual LLM to a new target language by initializing the token embeddings of the target language using a weighted average of semantically similar token embeddings from the source language. For this, we leverage a translation resource covering both the source and target languages. We validate our method with the Tweeties, a series of trans-tokenized LLMs, and demonstrate their competitive performance on various downstream tasks across a small but diverse set of languages.
BPE-Knockout
Pruning Pre-existing BPE Tokenisers with Backwards-compatible Morphological Semi-supervision
Byte-pair encoding (BPE) has become the default subword tokeniser in language models (LMs), allowing the representation of an infinite space of text with a finite set of units. Yet, BPE training is unsupervised, receiving no explicit information about a language's morphology. This results in a subword vocabulary wherein many units are a concatenation of partial morphemes, preventing their formation as tokens.
Tweety-7b-dutch
A Dutch generative LLM
Most Dutch generative language models start from an English or multilingual model and finetune that, which works well but is not optimal as the tokens are mostly English. We present Tweety-7b-dutch, a Dutch generative language model that is <i>trans-tokenized</i> to use Dutch tokens instead of English. To highlight the benefits of our method, we show that this model outperforms the multilingual and state-of-the-art Dutch generative language models.
Dutch Chat Toolkit
Creating retrieval-augmented chatbots
A lot of NLP technologies are easy to use for beginners, but creating and deploying a chatbot is still a bit tricky. Let's make a Python CLI toolkit to quickly create a chatbot with a web-based user interface.
RobBERT-2023
Updated large and base Dutch BERT models
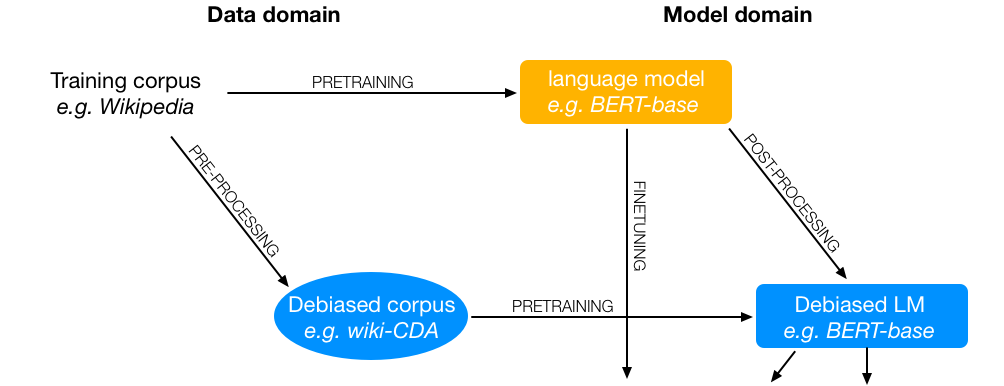
With RobBERT-2023, we deliver a freshly pre-trained Dutch tokenizer using the latest version of the Dutch OSCAR corpus. This corpus incorporates new high-frequency terms, such as those related to the COVID-19 pandemic, cryptocurrencies, and the ongoing energy crisis, while mitigating the inclusion of previously over-represented terms from adult-oriented content. Unlike the prior versions of RobBERT, which relied on the training methodology of RoBERTa but required a fresh weight initialization, RobBERT-2023 is entirely initialized using the RoBERTa-large model.
ResumeTailor
Improving Resume Quality Through Co-Creative Tools
Clear and well-written resumes can help jobseekers find better and better-suited jobs. However, many people struggle with writing their resumes, especially if they just entered the job market. Although many tools have been created to help write resumes, an analysis we conducted showed us that these tools focus mainly on layout and only give very limited content-related support. We present a co-creative resume building tool that provides tailored advice to jobseekers based on a comprehensive computational analysis of 444k resumes and the development of a Dutch language model, ResumeRobBERT, to provide contextual suggestions.
How far can it go?
On Intrinsic Gender Bias Mitigation for Text Classification
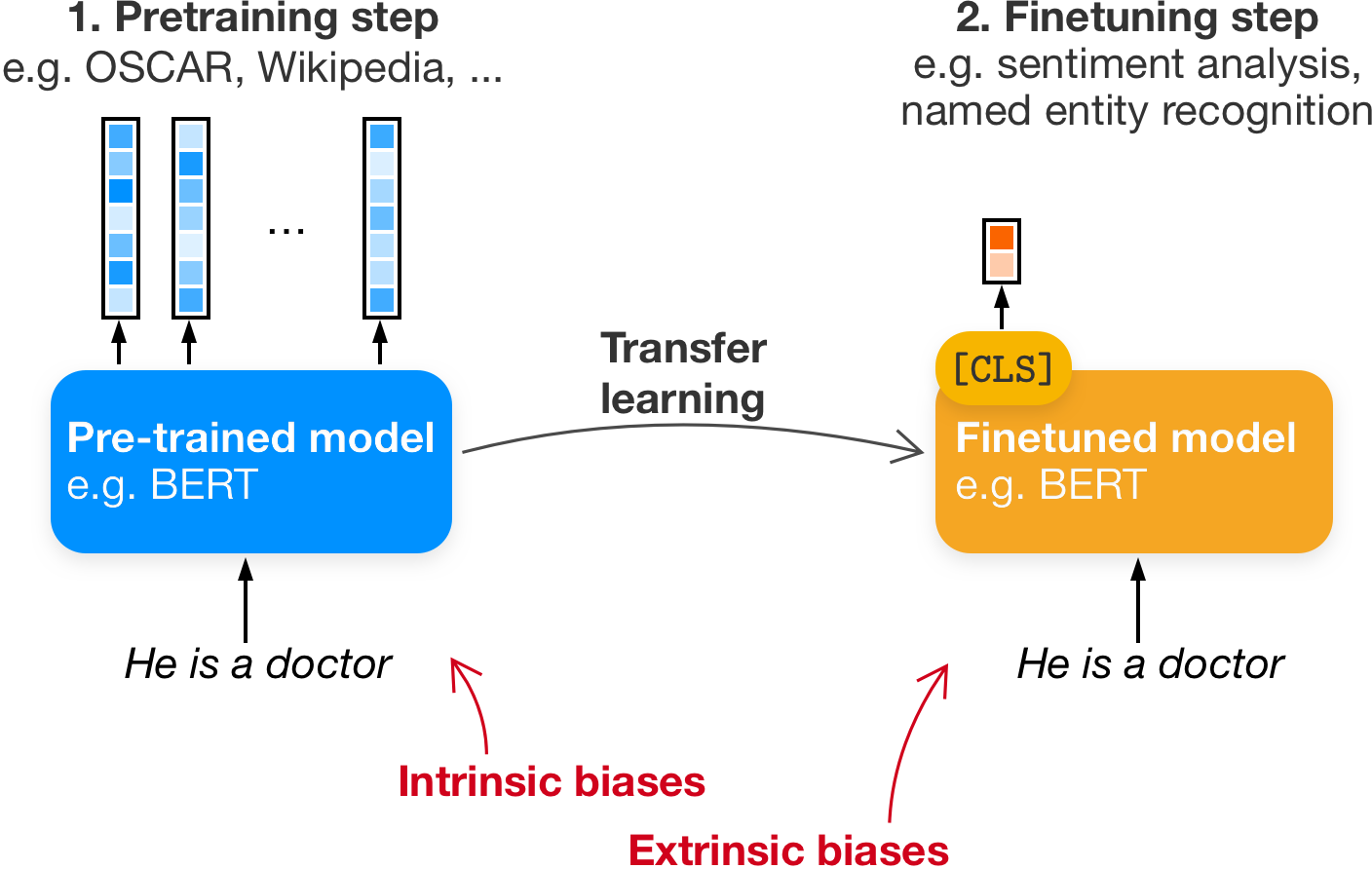
We have designed a probe to investigate the effects of intrinsic gender bias mitigation strategies on downstream text classification tasks. We find that instead of resolving gender bias, these strategies are able to hide it while retaining significant gender information in the embeddings. Based on these findings, we recommend that intrinsic bias mitigation techniques should be combined with other fairness interventions for downstream tasks.
RobBERT-2022
Updating a Dutch Language Model to Account for Evolving Language Use
We update the RobBERT Dutch language model to include new high-frequent tokens present in the latest Dutch OSCAR corpus from 2022. We then pre-train the RobBERT model using this dataset. Our new model is a plug-in replacement for RobBERT and results in a significant performance increase for certain language tasks.
FairDistillation
Mitigating Stereotyping in Language Models
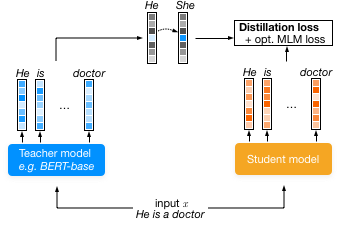
Large pre-trained language models are successfully being used in a variety of tasks, across many languages. With this ever-increasing usage, the risk of harmful side effects also rises, for example by reproducing and reinforcing stereotypes. However, detecting and mitigating these harms is difficult to do in general and becomes computationally expensive when tackling multiple languages or when considering different biases. To address this, we present FairDistillation : a cross-lingual method based on knowledge distillation to construct smaller language models while controlling for specific biases.
Measuring Fairness with Biased Rulers
A Survey on Quantifying Biases in Pretrained Language Models
An increasing awareness of biased patterns in natural language processing resources, like BERT, has motivated many metrics to quantify 'bias' and 'fairness'. But comparing the results of different metrics and the works that evaluate with such metrics remains difficult, if not outright impossible. We survey the existing literature on fairness metrics for pretrained language models and experimentally evaluate compatibility, including both biases in language models as in their downstream tasks. We do this by a mixture of traditional literature survey and correlation analysis, as well as by running empirical evaluations. We find that many metrics are not compatible and highly depend on templates, attribute and target seeds and the choice of embeddings.
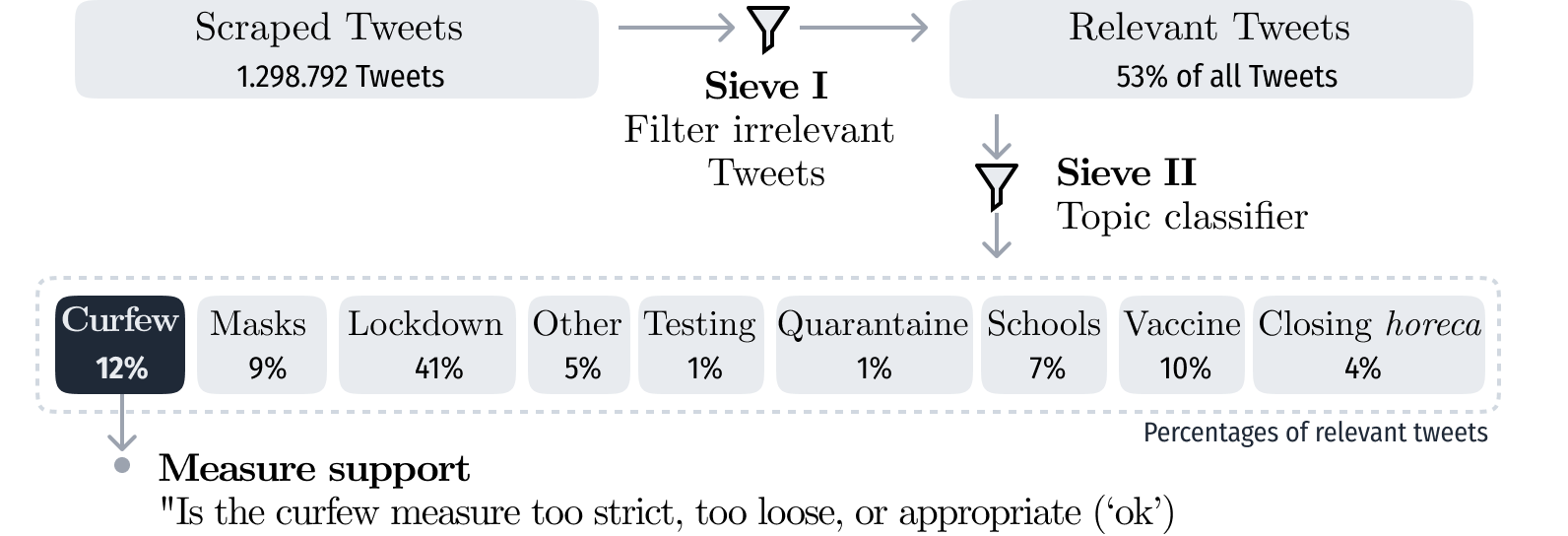
Attitudes Towards COVID-19 Measures
Measuring Shifts in Belgium Using Multilingual BERT
We classify seven months' worth of Belgian COVID-related Tweets using multilingual BERT and relate them to their governments' COVID measures. We classify Tweets by their stated opinion on Belgian government curfew measures (too strict, ok, too loose). We examine the change in topics discussed and views expressed over time and in reference to dates of related events such as implementation of new measures or COVID-19 related announcements in the media.
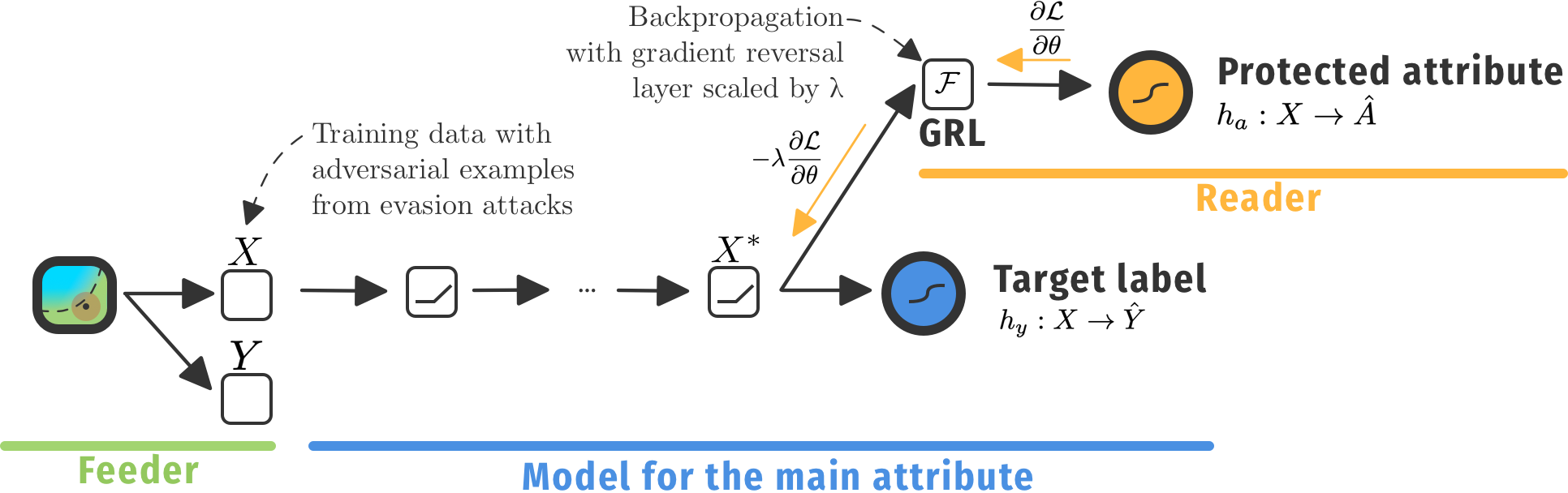
Ethical Adversaries
Towards Mitigating Unfairness with Adversarial Machine Learning
We offer a new framework that assists in mitigating unfair representations in the dataset used for training. Our framework relies on adversaries to improve fairness. First, it evaluates a model for unfairness w.r.t. protected attributes and ensures that an adversary cannot guess such attributes for a given outcome, by optimizing the model’s parameters for fairness while limiting utility losses. Second, the framework leverages evasion attacks from adversarial machine learning to perform adversarial retraining with new examples unseen by the model. We evaluated our framework on well-studied datasets in the fairness literature where it can surpass other approaches concerning demographic parity, equality of opportunity and also the model’s utility.
RobBERT
A Dutch RoBERTa-based Language Model
RobBERT is the state-of-the-art Dutch BERT model. It is a large pre-trained general Dutch language model that can be fine-tuned on a given dataset to perform any text classification, regression or token-tagging task. As such, it has been successfully used by many researchers and practitioners for achieving state-of-the-art performance for a wide range of Dutch natural language processing tasks.